How Much Current Draw 2n2222 Base

2N2222A in metal TO-18 parcel with the emitter, base and collector identified as E, B, and C respectively.

Cross section of 2N2222 in metal TO-eighteen package, showing connexion wires between external pins and die.
The 2N2222 is a common NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) used for general purpose low-power amplifying or switching applications. It is designed for low to medium current, low power, medium voltage, and tin can operate at moderately high speeds. Information technology was originally made in the TO-18 metal can every bit shown in the picture.
The 2N2222 is considered a very common transistor,[1] [ii] [3] and is used as an exemplar of an NPN transistor. It is oftentimes used as a modest-betoken transistor,[4] [v] and it remains a minor full general purpose transistor[6] of enduring popularity.[7] [eight] [9]
The 2N2222 was part of a family of devices described by Motorola at a 1962 IRE convention.[10] Since so it has been fabricated by many semiconductor companies, for instance, Texas Instruments.[xi]
Specifications [edit]
The JEDEC registration of a device number ensures item rated values volition be met past all parts offered under that number. JEDEC registered parameters include outline dimensions, pocket-size-indicate current gain, transition frequency, maximum values for voltage withstand, current rating, power dissipation and temperature rating, and others, measured under standard test conditions. Other office numbers will have different parameters. The exact specifications depend on the manufacturer, case type, and variation. Therefore, it is important to refer to the datasheet for the exact part number and manufacturer.
| Manufacturer | Vce | Ic | PD | fT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST Microminiaturization[12] 2N2222A | 40 V | 800 mA | 500 mW/1.8 W | 300 MHz |
All variations have a beta or current gain (hfe) of at to the lowest degree 100 in optimal weather condition. It is used in a diversity of analog amplification and switching applications.
Other switching transistors [edit]

Pinout of 2N2222 variants in plastic TO-92 package.
NPN silicon transistors with similar properties are also made in a variety of small through-hole and surface mountain packages including TO-92, SOT-23, and SOT-223.
Replacements for the 2N2222 are commonly available in the cheaper TO-92 packaging, where it is known as the PN2222 or P2N2222, which has like specifications except for the lower maximum collector current.[13] The P2N2222 has a dissimilar lodge of pins than the metal case 2N2222, with its emitter and collector connections switched; other plastic-example transistors as well accept different pinouts.
Single transistors are besides available in several different surface mount packages, and a number of manufacturers market place surface mount packages that comprise several 2N2222-type transistors in 1 package equally an array of transistors. The general specifications of the various variants are similar, with the biggest difference being the maximum allowable current and ability dissipation.
The BC548 family, including the BC547A to BC550C, are lower voltage, lower current, general-purpose transistors in TO-92 packages, originating in Europe, that are ofttimes found in small-signal distension and switching circuits of the type where the 2N2222 might otherwise exist used. They are not true replacements, only comparable devices that may be substituted but in circuits where the maximum current and voltage ratings are not exceeded.
The 2N2907 is an equally pop PNP transistor complementary to the 2N2222.[xiv]
The 2N3904 is an NPN transistor that can just switch one-tertiary the electric current of the 2N2222 but has otherwise like characteristics. The 2N3904 exhibits its forward gain (beta) tiptop at a lower current than the 2N2222, and is useful in amplifier applications with reduced Ic, e.g., (gain peak at ten mA for the 2N3904 only 150 mA for the 2N2222).
A version of the 2N2222A in a larger metallic TO-39 case, the 2N2219A had a higher ability dissipation rating (3 Watts when attached to a heatsink that keeps the case temperature at 25 C, or 0.8 Watts in free air, compared with but ane.8 Watts and 0.5 Watts (respectively) for the 2N2222A.[ citation needed ]
Part numbers [edit]
The 2N2222 (NPN) and 2N2907 (PNP) are complementary transistor pairs.
| BJT | Thru-hole | Surface-mount | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TO 18 | SOT23 | SOT223 | |
| NPN | 2N2222 | MMBT2222 | PZT2222A |
| PNP | 2N2907 | MMBT2907 | PZT2907A |
Photo Gallery [edit]
Various 2N2222 silicon dies
-

Motorola 2N2222 silicon dice
-

IPRS Baneasa 2N2222 silicon die
-
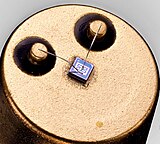
ITT Semiconductors 2N2222A silicon dice
-

CRP Industries 2N2222A silicon die
-

National Semiconductor 2N2222A silicon die
See also [edit]
- 2N3906
- 2N3055
- BC108
- BC548
- KT315
References [edit]
- ^ Dan O'Sullivan, Tom Igoe; "Physical Computing"; Cengage Learning; pp.nineteen; 2004; ISBN ane-59200-346-X
- ^ Brad Graham, Kathy McGowan; "Listen Operation Projects for the Evil Genius"; McGraw Hill Professional person; pp.18; 2010; ISBN 978-0-07-162392-6
- ^ Brad Graham, Kathy McGowan; "51 Loftier-Tech Practical Jokes for the Evil Genius"; McGraw Hill Professional person; pp.12; 2007; ISBN 978-0-07-149494-half dozen
- ^ Gordon McComb; "The Robot Builder's Bonanza"; McGraw-Loma Professional; 2001; pp.261; ISBN 978-0-07-136296-2
- ^ William Rynone; "Linear Active Circuits — Design and Analysis"; Artech House; pp.19; 1986; ISBN 0-89006-199-8
- ^ Dennis Barnaal, "Analog and Digital Electronics for Scientific Application"; Breton Publishers; pp.301; 1982; ISBN 0-534-01044-X
- ^ Rudolf F. Graf and William Sheets (2001). Build your ain low-power transmitters: projects for the electronics experimenter. Newnes. p. xiv. ISBN978-0-7506-7244-3.
The 2N2222, 2N2905, and 2N3055 devices, for example, which date back to the 1960s but have been improved, are still useful in new designs and are still popular for experimenters.
- ^ Ed Da Silva (2001). High frequency and microwave engineering science. Newnes. p. 263. ISBN978-0-7506-5046-5.
Typical examples are the well known NPN and PNP industrial and military types, 2N2222 and 2N2907, which have been used for over four decades and are still being used in many designs.
- ^ Jack Ward. "THE Evolution OF THE 2N2222: The Most Successful and Widely Used Transistor Ever Developed!". The Transistor Museum. Archived from the original on 14 April 2011. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
Since its initial product launch by Motorola at the 1962 IRE Convention, the 2N2222 has become the almost widely used and universally recognized transistor of all time. Billions of units take been manufactured over the past 45 years and in that location is continuing high volume annual production.
- ^ http://world wide web.semiconductormuseum.com/Transistors/Motorola/Haenichen/Haenichen_Page11.htm Haenichen oral history retrieved from the Semiconductor Museum 2011 May 13
- ^ The Transistor and Diode Data Book for Design Engineers, Texas Instruments Incorporated, no engagement, TI publication number CC413 71242-73-CSS, page four-93
- ^ http://www.st.com/st-web-ui/static/active/en/resources/technical/document/datasheet/CD00003223.pdf Datasheet accessed 2013-10-26
- ^ http://www.fairchildsemi.com/ds/PN/PN2222.pdf Archived 27 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 3 June 2012
- ^ Dave Hrynkiw and Mark W. Tilden (2002). Junkbots, bugbots, and bots on wheels: edifice simple robots with Beam technology. McGraw-Hill Professional. p. 44. ISBN978-0-07-222601-0.
Learn to keep an eye open for the post-obit transistors, as they're among the most useful, cheap, and popular types: PN2222/PN2907 These are general-purpose NPN/PNP transistors that can drive some practiced amounts of power. They're listed together because they're complementary transistors.
Further reading [edit]
- Historical Databooks
- Minor-Bespeak Semiconductors Information Book, 1218 pages, 1987, Motorola.
- Semiconductor Information Book, 916 pages, 1965, Motorola.
- Transistor and Diode Information Book, 1236 pages, 1973, Texas Instruments.
External links [edit]
| | Wikimedia Commons has media related to 2N2222. |
- Datasheet for 2N2222A How-do-you-do-reliability equivalent (PDF) by Microsemi
- Datasheet for Fairchild Semiconductor's equivalent PN2222 (PDF)
- 2N2222 Transistor History, Packaging and Datasheet
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2N2222
Posted by: mendozawailly64.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Much Current Draw 2n2222 Base"
Post a Comment